Problem #WSP-5523
Problem
A ball enters a wedge \(ABC\), striking the wall at \(A\) with an angle \(\alpha\), as shown in the diagram below.
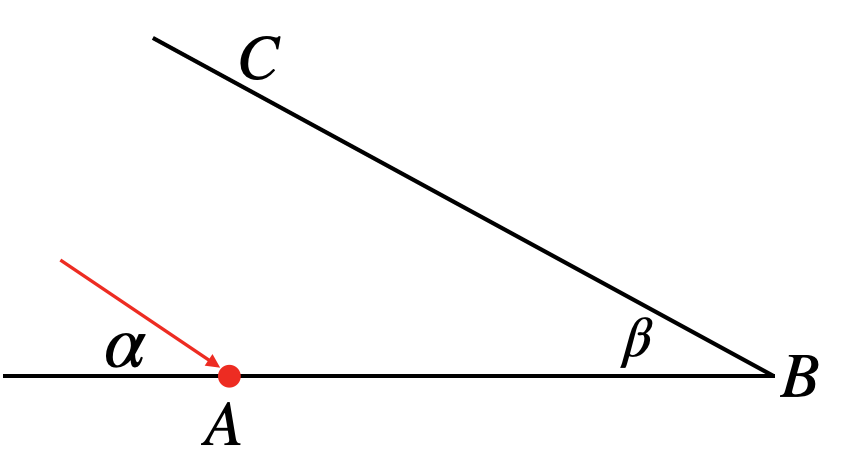
The wedge angle \(\angle ABC\) is \(\beta\). The ball keeps bouncing between the two walls until it eventually makes its last bounce (you can imagine that the sides \(AB\) and \(AC\) extend infinitely).
Find, in terms of \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\), how many times the ball bounces off the walls.
To see the solution register and get verified.