Problems
Find all functions \(f (x)\) defined for all positive \(x\), taking positive values and satisfying the equality \(f (x^y) = f (x)^f (y)\) for any positive \(x\) and \(y\).
The function \(f (x)\) is defined and satisfies the relationship \((x-1) f((x=1)/(x-1)) - f (x) = x\) for all \(x \neq 1\). Find all such functions.
Find all the functions \(f\colon \mathbb {R} \rightarrow \mathbb {R}\) which satisfy the inequality \(f (x + y) + f (y + z) + f (z + x) \geq 3f (x + 2y + 3z)\) for all \(x, y, z\).
Is there a bounded function \(f\colon \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) such that \(f (1)> 0\) and \(f (x)\) satisfies the inequality \(f^2 (x + y) \geq f^2 (x) + 2f (xy) + f^2 (y)\) for all \(x, y \in \mathbb{R}\)?
For which \(\alpha\) does there exist a function \(f\colon \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) that is not a constant, such that \(f (\alpha (x + y)) = f (x) + f (y)\)?
On a function \(f (x)\) defined on the whole line of real numbers, it is known that for any \(a > 1\) the function \(f (x)\) + \(f (ax)\) is continuous on the whole line. Prove that \(f (x)\) is also continuous on the whole line.
Does there exist a function \(f (x)\) defined for all \(x \in \mathbb{R}\) and for all \(x, y \in \mathbb{R}\) satisfying the inequality \(| f (x + y) + \sin x + \sin y | < 2\)?
The functions \(f (x) - x\) and \(f (x^2) - x^6\) are defined for all positive \(x\) and increase. Prove that the function
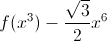
also increases for all positive \(x\).
A continuous function \(f(x)\) is such that for all real \(x\) the following inequality holds: \(f(x^2) - (f (x))^2 \geq 1/4\). Is it true that the function \(f(x)\) necessarily has an extreme point?
Let \(f\) be a continuous function defined on the interval \([0; 1]\) such that \(f (0) = f (1) = 0\). Prove that on the segment \([0; 1]\) there are 2 points at a distance of 0.1 at which the function \(f 4(x)\) takes equal values.