Problems
Cut the interval \([-1, 1]\) into black and white segments so that the integrals of any a) linear function; b) a square trinomial in white and black segments are equal.
Peter has 28 classmates. Each 2 out of these 28 have a different number of friends in the class. How many friends does Peter have?
\(x_1\) is the real root of the equation \(x^2 + ax + b = 0\), \(x_2\) is the real root of the equation \(x^2 - ax - b = 0\).
Prove that the equation \(x^2 + 2ax + 2b = 0\) has a real root, enclosed between \(x_1\) and \(x_2\). (\(a\) and \(b\) are real numbers).
With a non-zero number, the following operations are allowed: \(x \rightarrow \frac{1+x}{x}\), \(x \rightarrow \frac{1-x}{x}\). Is it true that from every non-zero rational number one can obtain each rational number with the help of a finite number of such operations?
At all rational points of the real line, integers are arranged. Prove that there is a segment such that the sum of the numbers at its ends does not exceed twice the number on its middle.
Prove that for any positive integer \(n\) the inequality
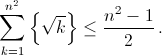
is true.
For which \(\alpha\) does there exist a function \(f\colon \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) that is not a constant, such that \(f (\alpha (x + y)) = f (x) + f (y)\)?
Given a square trinomial \(f (x) = x^2 + ax + b\). It is known that for any real \(x\) there exists a real number \(y\) such that \(f (y) = f (x) + y\). Find the greatest possible value of \(a\).
We are given a polynomial \(P(x)\) and numbers \(a_1\), \(a_2\), \(a_3\), \(b_1\), \(b_2\), \(b_3\) such that \(a_1a_2a_3 \ne 0\). It turned out that \(P (a_1x + b_1) + P (a_2x + b_2) = P (a_3x + b_3)\) for any real \(x\). Prove that \(P (x)\) has at least one real root.
It is known that a certain polynomial at rational points takes rational values. Prove that all its coefficients are rational.