Problems
Numbers \(a, b, c\) are integers with \(a\) and \(b\) being coprime. Let us assume that integers \(x_0\) and \(y_0\) are a solution for the equation \(ax + by = c\).
Prove that every solution for this equation has the same form \(x = x_0 + kb\), \(y = y_0 - ka\), with \(k\) being a random integer.
There are 13 weights. It is known that any 12 of them could be placed in 2 scale cups with 6 weights in each cup in such a way that balance will be held.
Prove the mass of all the weights is the same, if it is known that:
a) the mass of each weight in grams is an integer;
b) the mass of each weight in grams is a rational number;
c) the mass of each weight could be any real (not negative) number.
Can there exist two functions \(f\) and \(g\) that take only integer values such that for any integer \(x\) the following relations hold:
a) \(f (f (x)) = x\), \(g (g (x)) = x\), \(f (g (x)) > x\), \(g (f (x)) > x\)?
b) \(f (f (x)) < x\), \(g (g (x)) < x\), \(f (g (x)) > x\), \(g (f (x)) > x\)?
A student did not notice the multiplication sign between two three-digit numbers and wrote one six-digit number, which turned out to be exactly seven times their product. Determine these numbers.
The student did not notice the multiplication sign between two seven-digit numbers and wrote one fourteen-digit number, which turned out to be three times bigger than their product. Determine these numbers.
For each pair of real numbers \(a\) and \(b\), consider the sequence of numbers \(p_n = \lfloor 2 \{an + b\}\rfloor\). Any \(k\) consecutive terms of this sequence will be called a word. Is it true that any ordered set of zeros and ones of length \(k\) is a word of the sequence given by some \(a\) and \(b\) for \(k = 4\); when \(k = 5\)?
Note: \(\lfloor c\rfloor\) is the integer part, \(\{c\}\) is the fractional part of the number \(c\).
Prove that for any natural number \(a_1> 1\) there exists an increasing sequence of natural numbers \(a_1, a_2, a_3, \dots\), for which \(a_1^2+ a_2^2 +\dots+ a_k^2\) is divisible by \(a_1+ a_2+\dots+ a_k\) for all \(k \geq 1\).
At all rational points of the real line, integers are arranged. Prove that there is a segment such that the sum of the numbers at its ends does not exceed twice the number on its middle.
Prove that for any positive integer \(n\) the inequality
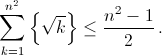
is true.
Find the sum \(1/3 + 2/3 + 2^2/3 + 2^3/3 + \dots + 2^{1000}/3\).