Problems
Let \(n\) numbers are given together with their product \(p\). The difference between \(p\) and each of these numbers is an odd number.
Prove that all \(n\) numbers are irrational.
a) Could an additional \(6\) digits be added to any \(6\)-digit number starting with a \(5\), so that the \(12\)-digit number obtained is a complete square?
b) The same question but for a number starting with a \(1\).
c) Find for each \(n\) the smallest \(k = k (n)\) such that to each \(n\)-digit number you can assign \(k\) more digits so that the resulting \((n + k)\)-digit number is a complete square.
Two players in turn paint the sides of an \(n\)-gon. The first one can paint the side that borders either zero or two colored sides, the second – the side that borders one painted side. The player who can not make a move loses. At what \(n\) can the second player win, no matter how the first player plays?
Jane wrote another number on the board. This time it was a two-digit number and again it did not include digit 5. Jane then decided to include it, but the number was written too close to the edge, so she decided to t the 5 in between the two digits. She noticed that the resulting number is 11 times larger than the original. What is the sum of digits of the new number?
a) Find the biggest 6-digit integer number such that each digit, except for the two on the left, is equal to the sum of its two left neighbours.
b) Find the biggest integer number such that each digit, except for the rst two, is equal to the sum of its two left neighbours. (Compared to part (a), we removed the 6-digit number restriction.)
Tile a \(5\times6\) rectangle in an irreducible way by laying \(1\times2\) rectangles.
Does there exist an irreducible tiling with \(1\times2\) rectangles of a \(4\times 6\) rectangle?
Irreducibly tile a floor with \(1\times2\) tiles in a room that is a \(5\times8\) rectangle.
Tile the whole plane with the following shapes:
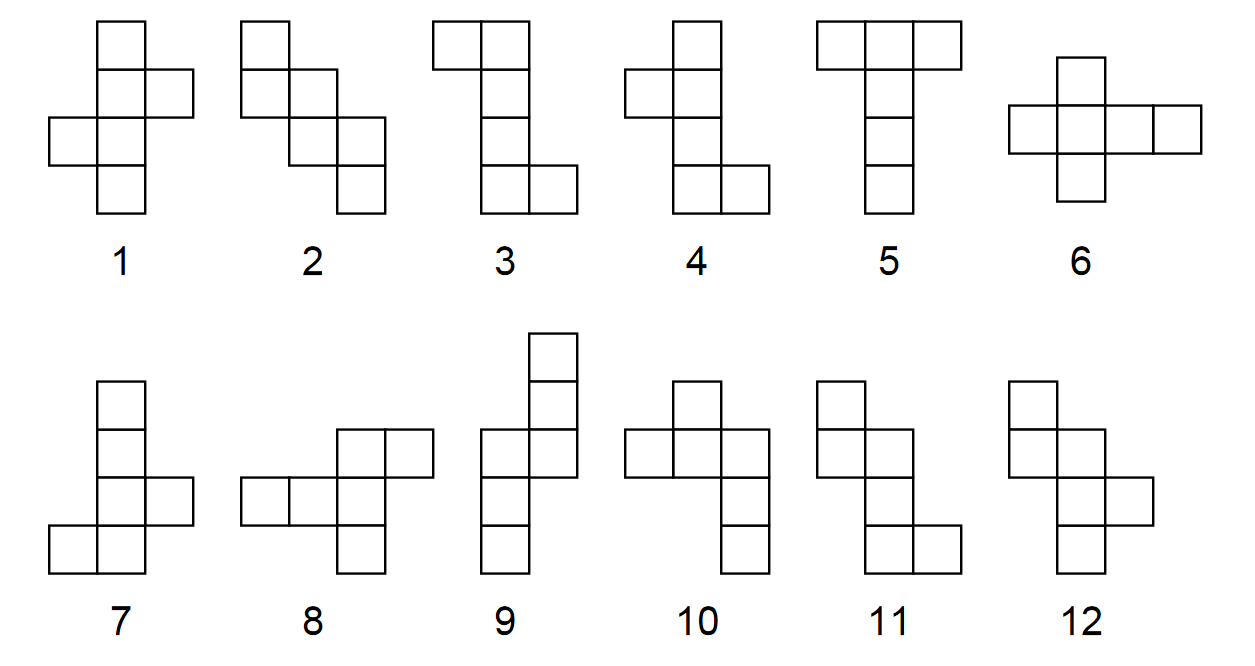
David Smith cut out 12 nets. He claimed that it was possible to make a cube out of each net. Roger Penrose looked at the patterns, and after some considerable thought decided that he was able to make cubes from all the nets except one. Can you figure out which net cannot make a cube?