Problems
A regular dice is thrown many times. Find the mathematical expectation of the number of rolls made before the moment when the sum of all rolled points reaches 2010 (that is, it became no less than 2010).
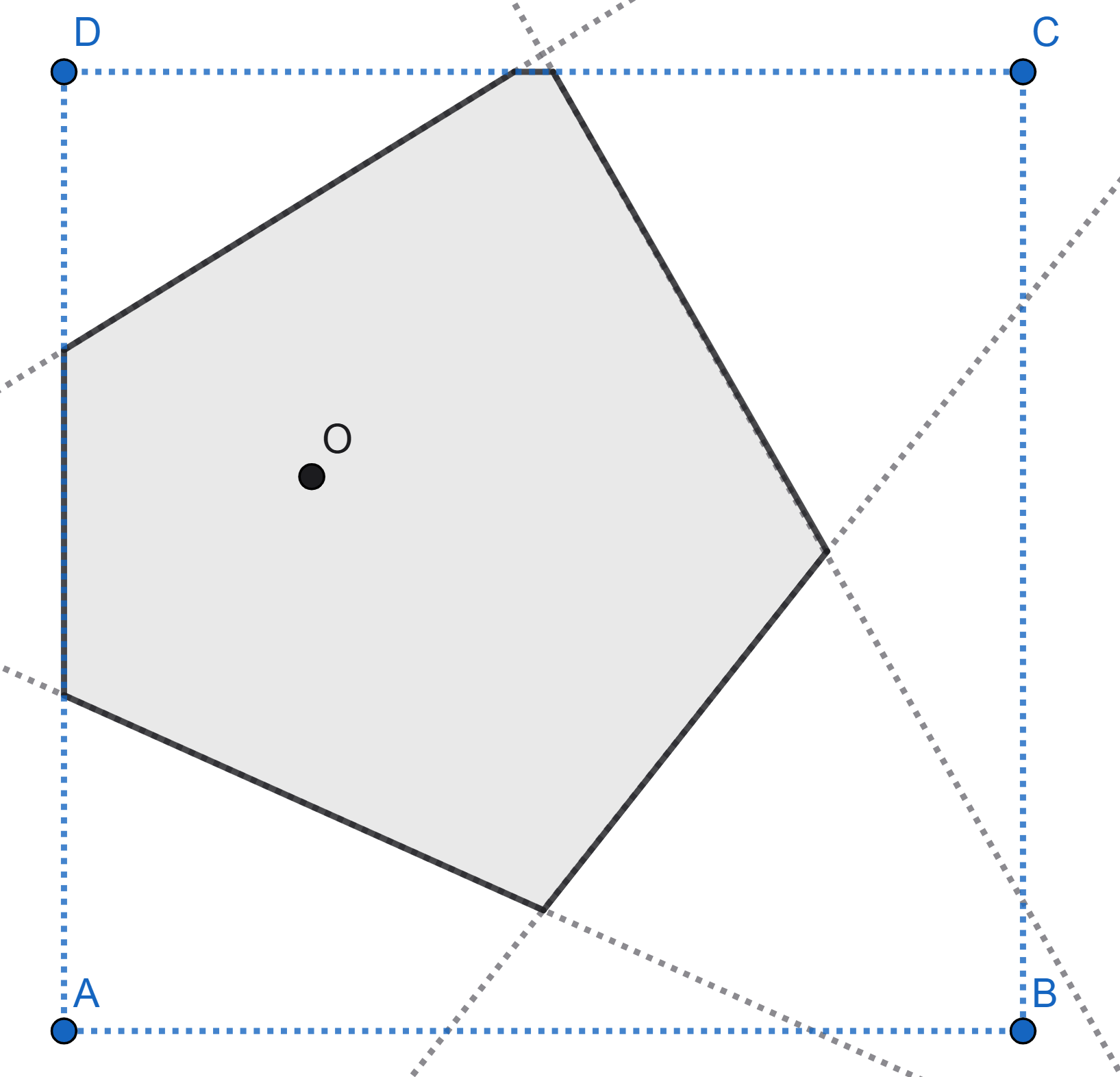
The point \(O\) is randomly chosen on piece of square paper. Then the square is folded in such a way that each vertex is overlaid on the point \(O\). The figure shows one of the possible folding schemes. Find the mathematical expectation of the number of sides of the polygon that appears.
The bus has \(n\) seats, and all of the tickets are sold to \(n\) passengers. The first to enter the bus is the Scattered Scientist and, without looking at his ticket, takes a random available seat. Following this, the passengers enter one by one. If the new passenger sees that his place is free, he takes his place. If the place is occupied, then the person who gets on the bus takes the first available seat. Find the probability that the passenger who got on the bus last will take his seat according to his ticket?
A fair dice is thrown many times. It is known that at some point the total amount of points became equal to exactly 2010.
Find the mathematical expectation of the number of throws made to this point.
In the city where the Scattered Scientist lives, telephone numbers consist of 7 digits. The scientist easily remembers a phone number, if this number is a palindrome, that is, it is identical when read from left to right and from right to left. For example, the number 4435344 the scientist remembers easily, because this number is a palindrome. And the number 3723627 is not a palindrome, so the scientist does not remember this number easily. Find the probability that the scientist will remember the phone number of a new random acquaintance easily.
Ben is going to bend a square sheet of paper \(ABCD\). Ben calls the fold beautiful, if the side \(AB\) crosses the side \(CD\) and the four resulting rectangular triangles are equal. Before that, Jack selects a random point on the sheet \(F\). Find the probability that Ben will be able to make a beautiful fold through the point \(F\).
The Scattered Scientist constructed a device consisting of a sensor and a transmitter. The average life expectancy of the sensor part is 3 years, the average lifetime of the transmitter is 5 years. Knowing the distribution of the lifetime of the sensor and the transmitter, the Scattered Scientist calculated that the average lifetime of the entire device is 3 years 8 months. Was the Scattered Scientist wrong in his calculations?
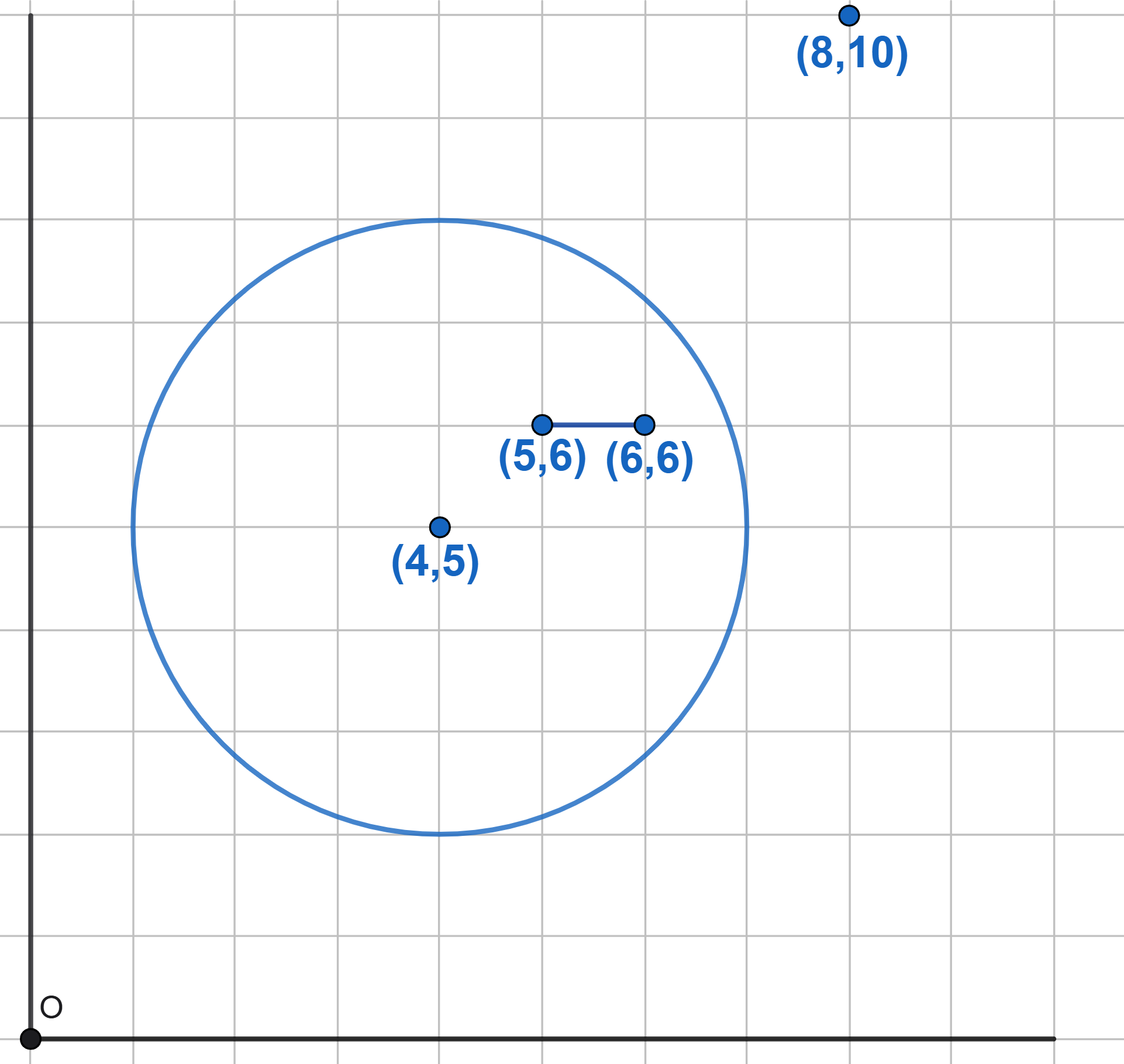
A fly crawls along a grid from the origin. The fly moves only along the lines of the integer grid to the right or upwards (monotonic wandering). In each node of the net, the fly randomly selects the direction of further movement: upwards or to the right. Find the probability that at some point:
a) the fly will be at the point \((8, 10)\);
b) the fly will be at the point \((8, 10)\), along the line passing along the segment connecting the points \((5, 6)\) and \((6, 6)\);
c) the fly will be at the point \((8, 10)\), passing inside a circle of radius 3 with center at point \((4, 5)\).
The television game “What? Where? When?” consists of a team of “experts” trying to solve 13 questions that are thought up and sent in by the viewers of the programme. Envelopes with the questions are selected in turn in random order with the help of a spinning top with an arrow. If the experts answer correctly, they earn a point, and if they answer incorrectly, the viewers get one point. The game ends as soon as one of the teams scores 6 points. The probability of the team of experts winning in one round is 0.6 and there can be no draws. Currently, the experts are losing 3 to 4. Find the probability that the experts will still win.
A fly moves from the origin only to the right or upwards along the lines of the integer grid (a monotonic wander). In each node of the net, the fly randomly selects the direction of further movement: upwards or to the right.
a) Prove that sooner or later the fly will reach the point with abscissa 2011.
b) Find the mathematical expectation of the ordinate of the fly at the moment when the fly reached the abscissa 2011.