Problems
Replace \(a, b\) and \(c\) with integers not equal to \(1\) in the equality \((ay^b)^c = - 64y^6\), so it would become an identity.
Prove that for any natural number \(a_1> 1\) there exists an increasing sequence of natural numbers \(a_1, a_2, a_3, \dots\), for which \(a_1^2+ a_2^2 +\dots+ a_k^2\) is divisible by \(a_1+ a_2+\dots+ a_k\) for all \(k \geq 1\).
At all rational points of the real line, integers are arranged. Prove that there is a segment such that the sum of the numbers at its ends does not exceed twice the number on its middle.
Prove that for any positive integer \(n\) the inequality
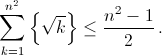
is true.
Find the sum \(1/3 + 2/3 + 2^2/3 + 2^3/3 + \dots + 2^{1000}/3\).
A numeric set \(M\) containing 2003 distinct numbers is such that for every two distinct elements \(a, b\) in \(M\), the number \(a^2+ b\sqrt 2\) is rational. Prove that for any \(a\) in \(M\) the number \(q\sqrt 2\) is rational.
Does there exist a function \(f (x)\) defined for all \(x \in \mathbb{R}\) and for all \(x, y \in \mathbb{R}\) satisfying the inequality \(| f (x + y) + \sin x + \sin y | < 2\)?
The functions \(f (x) - x\) and \(f (x^2) - x^6\) are defined for all positive \(x\) and increase. Prove that the function
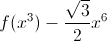
also increases for all positive \(x\).
The quadratic trinomials \(f (x)\) and \(g (x)\) are such that \(f' (x) g' (x) \geq | f (x) | + | g (x) |\) for all real \(x\). Prove that the product \(f (x) g (x)\) is equal to the square of some trinomial.
Prove that if the numbers \(x, y, z\) satisfy the following system of equations for some values of \(p\) and \(q\): \[\begin{aligned} y &= x^2 + px + q,\\ z &= y^2 + py + q,\\ x &= z^2 + pz + q, \end{aligned}\] then the inequality \(x^2y + y^2z + z^2x \geq x^2z + y^2x + z^2y\) is satisfied.